Today.Az » Weird / Interesting » New species of ancient predatory fish discovered
13 September 2011 [16:06] - Today.Az
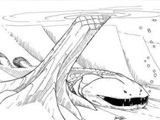 The Academy of Natural Sciences has announced the discovery of a new species of large predatory fish that prowled ancient North American waterways during the Devonian Period, before backboned animals existed on land.
The Academy of Natural Sciences has announced the discovery of a new species of large predatory fish that prowled ancient North American waterways during the Devonian Period, before backboned animals existed on land.
Drs. Edward "Ted" Daeschler and Jason Downs of the Academy and
colleagues from the University of Chicago and Harvard University
describe the new denizen of the Devonian they named Laccognathus embryi in the current issue of the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
The 375-million-year-old beast was discovered by the same group of
researchers who discovered Tiktaalik roseae, the important transitional
animal considered "a missing link" between fish and the earliest limbed
animals. The fossil remains of the new species were found at the same
site as Tiktaalik, on Ellesmere Island in the remote Nunavut Territory
of Arctic Canada.
The Devonian Period (415 to 360 million years ago) is often described
as the Age of Fishes because of the rich variety of aquatic forms that
populated the ancient seas, lagoons and streams. Laccognathus embryi
is a lobe-finned fish whose closest living relative is the lungfish.
The creature probably grew to about 5 or 6 feet long and had a wide head
with small eyes and
robust jaws lined with large piercing teeth. "I wouldn't want to be
wading or swimming in waters where this animal lurked," said Daeschler,
co-author of the paper and the Academy's curator of vertebrate zoology.
"Clearly these Late Devonian ecosystems were vicious places, and
Laccognathus filled the niche of a large, bottom-dwelling, sit-and-wait
predator with a powerful bite."
The researchers named the new species in honor of Dr. Ashton Embry, a
Canadian geologist whose work in the Arctic islands paved the way for
the authors' paleontological explorations.
The kind of fish known as Laccognathus (translates as pitted
jaw) was previously only known from Eastern Europe. The discovery of
Laccognathus embryi, the new species, extends the geographic range of
Laccognathus to North America and confirms direct connection of the
North American and European landmasses during the Devonian Period.
"This study is the culmination of a lot of work in the field, in the
fossil lab, and in the office," said Downs, lead author of the study.
Downs, an Academy research associate and a visiting professor at
Swarthmore College, started studying fossils in high school as an
Academy volunteer.
"Our team collected the first fossils of Laccognathus
almost 10 years ago, and the collection has grown with each subsequent
field season. The quality and quantity of this collection will continue
to shed new light on these unusual animals."
Other scientists who collaborated on the new discovery are Dr. Farish
Jenkins Jr. of Harvard University and Dr. Neil Shubin of the University
of Chicago. The research was funded by the National Science Foundation
and the National Geographic Society.
/Science Daily/
|